Welcome to my blog Today’s post is a little different, it was written by me, however, the original article is published on DeliveryHero Techblog.
Check out the original article by clicking here.
Happy reading.
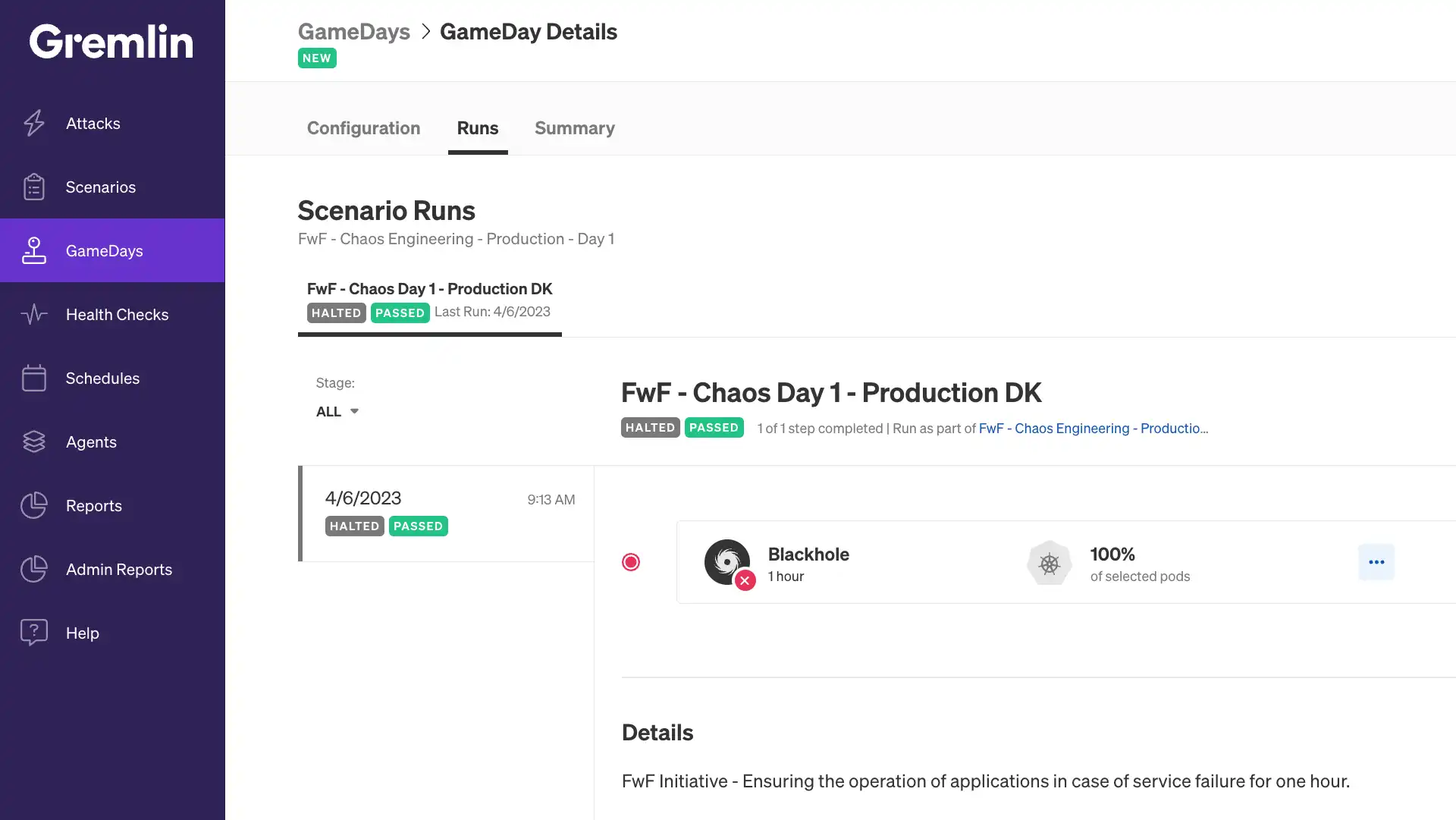
We challenged technology teams to test a long outage of a configuration application in a production environment for an hour without losing any requests using Chaos Engineering. And guess what? We did it!
How did we get here?
Over the past few months, our team has embarked on an exciting and challenging experiment in chaos engineering. Our goal was simple: understand the behaviour of our services and ensure the smooth operation of our applications in the event of a prolonged outage of a third-party application. The results were astonishing, and we are proud to share our findings with you in this blog post!
Como uma empresa que atende a milhões de usuários em todo o mundo, entendemos a importância de identificar proativamente os pontos fracos de nossos sistemas complexos. É por isso que seguimos os passos de gigantes da tecnologia como Google, Amazon e Netflix, adotando experimentos de engenharia do caos para garantir a confiabilidade e a resiliência.
Em anos anteriores, nossa plataforma sofreu perda de pedidos devido a problemas relacionados a sinalizadores de recursos e configurações. Determinados a resolver esses problemas, desafiamos nossos líderes de linha de produtos de tecnologia a testar uma longa interrupção de um aplicativo de configuração em um ambiente de produção por uma hora sem perder nenhum pedido. E adivinhe só? Conseguimos!
O experimento: Mergulhando no caos para fortalecer os aplicativos
Você já se perguntou como as empresas de tecnologia gerenciam e testam novos recursos em seus aplicativos antes de disponibilizá-los para os usuários finais? Ou mesmo como cada ambiente tem sua configuração específica de acordo com o local/região/país? Uma das práticas mais comuns é usar sistemas de gerenciamento de sinalizadores de recursos (flags). Neste experimento, exploramos como o uso da Chaos Engineering pode melhorar a resiliência de todo um ecossistema que usa um aplicativo de terceiros para configuração e/ou disponibilidade.

Chaos Engineering is a systematic approach to improving the resilience and reliability of a system by introducing controlled failures and disturbances into specific environments. This practice helps identify and solve problems before they cause unwanted disruptions, thus ensuring the system can cope with and adapt to different failure scenarios.
This way, teams can learn how systems react under pressure and improve their recovery capacity when facing adverse events, using the tool to reduce the blast radius. Some examples can be running tests in production during low-traffic hours, experimenting in staging environments, and experimenting on a specific percentage of application instances.
The Challenge: Putting the system to the test
To perform the proposed tests, we used the Gremlin Chaos Engineering tool, which allowed us to create blackhole attacks.

The concept of Blackhole, used by the Gremlin, refers to a technique that simulates a complete interruption in communication between the components of a distributed system. During a Blackhole attack, the Gremlin intercepts and discards all network traffic between affected services, creating a situation where the components cannot communicate amongst themselves, as if they were isolated in a black hole.
Using this approach, we can temporarily interrupt communication between the services involved, putting the system’s resilience and ability to recover from communication failures to the test. These assumptions reflect real problems that have been encountered on the platform in the past, so we were able to simulate the incident again and ensure that everything works as it should.
The Method: Striking at the core of the system
The Chaos tests started to be executed in controlled environments. There were six tests in development environments, simulating the scenario that we would have in production. This step was necessary so that we could minimize the blast radius and guarantee that the monitoring was adequate so that no detail would go unnoticed.
Throughout the experiment, we introduced a series of attacks known as Blackhole at different times and in a controlled way. This allowed us to observe how each application, which depended on the attacked service, behaved when an interruption occurred.
We were also able to understand which services had hidden dependencies on this service, as well as the bottlenecks that the lack of service could cause in applications. This approach helped us identify weaknesses and areas for improvement in the system.
The Results: Revealing hidden secrets
At the end of the experiment, we came across some surprising findings. We discovered that while the feature flag management application was robust in many ways, some specific areas needed attention. We identified real issues before they became incidents, potentially resulting in lost orders.
Among the problems encountered, we can cite the application of patches that collect new metrics aiming at observability, bug fixing related to latency increase, and a lack of valid configuration in case of failure to obtain the feature flag. In addition, the experiments brought about improvements in communication between internal third-party services, providing greater resilience to the system as a whole, including ways to work around failures in a real-life scenario.
Conclusion – The Future: Breaking new ground
This experience enabled us to demonstrate the power of Chaos Engineering in identifying and resolving issues before they can negatively affect end users, as well as ensuring that problem monitoring is adequate and that staff know what to do when a related problem occurs. This allows us to think proactively, identifying failures even before an incident occurs and no longer be reactive to problems during a change.
For our teams, the experiment gave us a better understanding of service behaviour and how we can improve our applications to solve unknown bugs, without losses. Based on one internal survey conducted after the production test, it is evident that the majority of respondents found chaos engineering experiments to be effective in uncovering potential system weaknesses or vulnerabilities.
60% indicated it was very effective, and 20% indicated it was extremely effective. Additionally, 80% of respondents agreed that the steps and procedures of the chaos engineering experiment were communicated and easy to follow.
The participants also expressed interest in delving deeper into Chaos Engineering in their respective teams. All participants indicated that they intend to conduct experiments in the near future as part of the application lifecycle.